Table of contents
DCP Inside is the result of two and a half years of work (with several interruptions…) started in early 2020 , based on intensive reading sessions of documentation, standards, norms, white-papers and theses on digital cinema, imagery and sound.
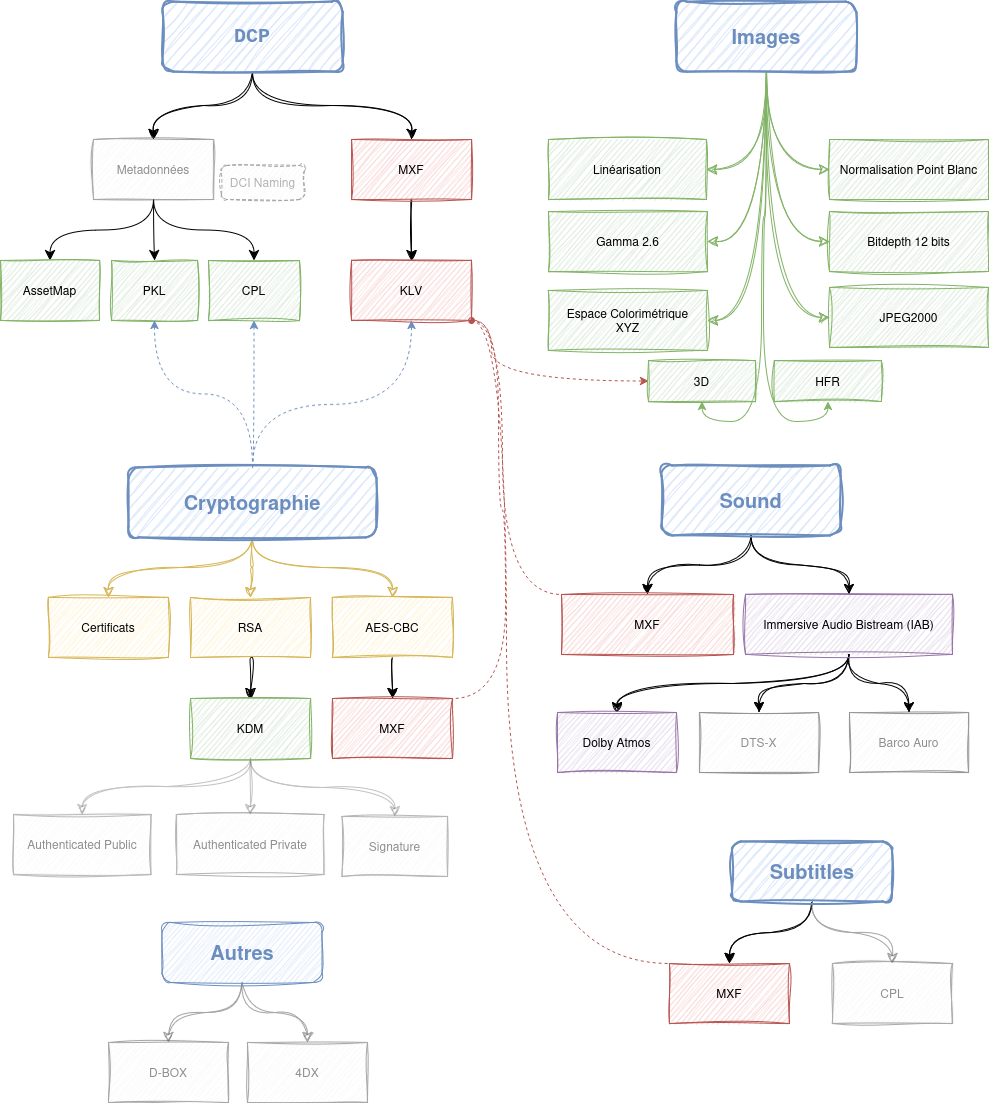
Here is the complete table of contents of all topics covered in DCP-Inside. The different chapters can be intertwined with each other. You will find a quick and graphic summary just below. Do not hesitate to browse the entire table of contents to discover chapters not mentioned in the graphic summary. (easter-eggs: some chapters are hidden for now, still in progress ;-)
You have the opportunity to leave annotations on the documentation (in case of mistakes or unclear paragraphs). The annotation sytem is persistent, your annotations will remain. You can edit or remove your annotations. If you wish, please, leave a contact address in case I need additional feedback :)
English version
Visual Overview
Chapter summary
History of Digital Cinema :
The Digital Cinema Package (DCP) :
DCP Metadata :
AssetMap :
AssetMap AssetMap : Codes & Fichiers Packing List (PKL) :
PKL : Packing List PKL : Codes & Fichiers Composition Playlist (CPL) :
CPL : Composition Playlist CPL : Les types d'assets CPL : AssetType : Generic CPL : AssetType : TrackFile CPL : AssetType : PictureTrackFile CPL : AssetType : SoundTrackFile CPL : AssetType : SubtitleTrackFile CPL : AssetType : CaptionTrackFile CPL : AssetType : CompositionMetadata CPL : AssetType : Marker CPL : AssetType : DataTrackFile CPL : Codes & Fichiers MXF : the assets
KLV : Length : La taille des données KLV : Value : Les données utiles KLV : Les types & formats KLV : Local Tag : Les mini-identifiants MXF : Operational Pattern : Les différents modèles de MXF MXF : KLV Headers :
Partition Pack Primer Pack Preface Identification Content Storage Essence Container Data Material Package Source Package Track et ses enfants Timeline Track Static Track Sequence Timecode Component Source Clip Descriptive Medata (DM) Segment Fill Item MXF : KLV Footers :
Index Table Segment Random Index Pack MXF : KLV depending on the type of data :
MXF : Picture : RGBA Essence Descriptor MXF : Picture : JPEG2000 Picture Sub-Descriptor MXF : Picture : Stereoscopique (3D) MXF : Picture : High Frame Rate (HFR) MXF : Sound MXF : Sound : Configuration Audio & Multichannel Audio (MCA) MXF : Subtitle : Les sous-titres (et ses compagnons) MXF : AuxData : Le containeur fourre-tout MXF : Dolby Atmos : Le son spatialisé MXF : D-Box : Le cinéma dynamique simple, les sièges mouvants, la gerbe au tournant MXF : Misc :
MXF : Codes & Fichiers Cryptographie in a DCP :
Cryptographie : L'algorithme symétrique AES-CBC Cryptographie : L'algorithme asymétrique RSA La cryptographie appliquée dans un MXF KDM : Digital Keys of films
KDM : Authenticated Public KDM : Authenticated Private KDM : Signature KDM : Codes & Fichiers Certificates : Digital Identification Papers
Certificats : Les champs (fields) d'un certificat x509 DCI Certificats : Identity Attributes : les attributs et leurs rôles Certificats : La chaîne de certification Certificats : Certificate Thumbprint Certificats : Public Key Thumbprint : dnQualifier Certificats : Création de nos propres certificats
Image :
JPEG2000 : Le format d'image utilisé dans le cinéma numérique MXF : Picture : Stereoscopique (3D) MXF : Picture : High Frame Rate (HFR) 3D HFR Sound :
MXF : Sound MXF : Sound : Configuration Audio & Multichannel Audio (MCA) Immersive Audio Bitstream (IAB) : Le parent du son spatialisé Dolby Atmos : Le son spatialisé MXF : Dolby Atmos : Le son spatialisé DTS-X : Le son spatialisé Barco Auro : Le son spatialisé Subtitle :
CPL : AssetType : SubtitleTrackFile CPL : AssetType : CaptionTrackFile MXF : Subtitle : Les sous-titres (et ses compagnons) Additional Assets :
Immersive Audio Bitstream (IAB) : Le parent du son spatialisé Dolby Atmos : Le son spatialisé DTS-X : Le son spatialisé Barco Auro : Le son spatialisé D-Box : Le cinéma dynamique simple, les sièges mouvants, la gerbe au tournant MXF : D-Box : Le cinéma dynamique simple, les sièges mouvants, la gerbe au tournant 4DX : Le cinéma dynamique complexe, les sièges mouvants, la gerbe au tournant
Misc :
Digital Cinema Naming Convention : Les noms des DCP (quasi) normés X-Files : Les informations inclassables ;-) Credits & Licence d'utilisation
Complete chaptering
Preface
Preambule
Tools and prototypes
Conclusion
History of Digital Cinema
Digital Cinema Initiative (DCI) : History & Creation
Preface
The prehistory of digital cinema : the electronic cinema
The beginning of standardization : the digital cinema
StEM : the short film for evaluation
StEm n°2 : Digivolution !
DCI Specifications
The technical decisions made by DCI
List of specifications and standards DCI / SMPTE
Ressources
The Digital Cinema Package (DCP)
DCP Metadata
Metadata are dispatched in AssetMap , PackingLists (PKL) and CompositionPlaylists (CPL).
AssetMap
AssetMap
Préface
Description
Schéma visuel de la structure XML
Explication de la structure XML
Explications des différents éléments
Cryptographie : Le grand manquant
Interop vs SMPTE
Notes
AssetMap : Codes & Fichiers
Les fichiers
Validation XML
Pour générer un UUID
Pour générer une date au format ISO
Pour parser une date au format ISO
Pour parser une date et la retourner au format ISO
Récupération d'élements dans une AssetMap
Récupération l'AnnotationText
Récupération des fichiers des différents assets
Récupération des identifiants (Id) des différents assets
Packing List (PKL)
PKL : Packing List
Préface
Description
Schéma visuel de la structure XML
Explication de la structure XML
Cryptographie : La signature de la PKL
Notes
PKL : Codes & Fichiers 2
Les fichiers
Validation XML
Récupération de l'identifiant (Id) d'une PKL
Récupération des informations des assets
Composition Playlist (CPL)
MXF : the assets
MXF : KLV Headers
Partition Pack
Préface
Description
Les métadonnées
Relation entre les différents partitions packs
Position de ces KLV dans un MXF
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Partition Pack
Primer Pack
Préface
Description
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Primer Pack
Notes
Preface
Préface
Description
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Preface
Identification
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Identification
Content Storage
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Content Storage
Essence Container Data
Préface
Les metadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Essence Container Data
Notes
Material Package
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Material Package
Source Package
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Source Package
Track et ses enfants
Timeline Track
Static Track
Timeline Track
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Timeline Track
Notes
Static Track
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Static Track
Notes
Sequence
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Sequence
Timecode Component
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Timecode Component
Source Clip
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de SourceClip
Descriptive Medata (DM) Segment
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données brutes du KLV
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de DM Segment
Fill Item
MXF : KLV Footers
Index Table Segment
Préface
Les métadonnées
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Index Table Segment
Random Index Pack
Preface
Les métadonnées
Etude rapide de l'Universal Label de Random Index Pack
MXF : KLV depending on the type of data
MXF : Picture 1
Preface
KLV Headers
KLV Body : Picture Essence
Code : Read and Extract the KLV "Picture Essence"
Code : Write own KLV Picture Essence
Cryptography
XYZ Colorimetry
JPEG2000 Encoding
Stereoscopic (3D)
High Frame Rate (HFR)
Notes
MXF : Picture : RGBA Essence Descriptor 2
Préface
Les métadonnées
Structures des données
Hiérarchie du format
Code : Lire ce KLV
La suite...
Notes
MXF : Picture : JPEG2000 Picture Sub-Descriptor 2
Préface
Les métadonnées
Structures des données
Hiérarchie du format
Lire ce KLV
MXF : Picture : Stereoscopique (3D) 1
Préface
Les métadonnées
Lire et extraire les images stéréoscopiques
Les modifications dans la Composition Playlist (CPL)
Faire de la stéréoscopie sans utiliser ce workflow
Comment faire de la 3D en HFR
Samples
MXF : Picture : High Frame Rate (HFR)
Préface
High Frame Rate (HFR) & Stéréoscopie (3D)
Samples
Notes
MXF : Sound 1
Préface
Les KLV de métadonnées (Partition Header)
Métadonnées supplémentaires : La configuration sonore & Multichannel Audio (MCA)
A l'intérieur du KLV Sound Essence
Création d'un header WAVE (Python)
Extraire la piste son au format WAV (Python)
Ecrire nos propres KLV
Techniques
Notes
MXF : Sound : Configuration Audio & Multichannel Audio (MCA)
Préface
Channel Assignment : Le point d'entrée
Les Sub-Descriptors Audios : Préface
Les Sub-Descriptors Audios : En détail
Channel Layout / Soundfield Groups Configuration : le statique dynamique statique
Conclusion
Notes
MXF : Subtitle : Les sous-titres (et ses compagnons)
Préface
Les métadonnées
Contenu d'un fichier sous-titres classique
Contenu d'un fichier sous-titres avec des images
Conclusion
Samples
Ressources annexes
Notes
MXF : AuxData : Le containeur fourre-tout
Préface
Dolby Atmos ?
DTS-X ?
Barco Auro ?
Notes
MXF : Dolby Atmos : Le son spatialisé 9
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données
A l'intérieur du IABitstream : Le container maître de base
A l'intérieur d'une IABitstream frame : l'unité de base
Les IAElements : Les blocs de métadonnées et de données utiles
Les différents éléments : Leurs structures internes
IABitstream frame
IAElement
IA Frame
Bed Definition : le câblage des pistes (Bed) avec les assets audios
Object Definition : les métadonnées de spatialisation
Bed Remap : Configuration pour du sous-mixage
Object Zone Definition : Les zones alternatives
Authoring Tool Info : Les informations créateurs
User Data : Les métadonnées personnelles
Audio Data PCM & DLC : les containers audio
Audio Data DLC : l'élu pour le DCP-IAB !
Audio Data PCM : le recalé du DCP-IAB
L'encodage Plex : les tailles dynamiques
Analyse du MXF
Annexes
Notes
MXF : D-Box : Le cinéma dynamique simple, les sièges mouvants, la gerbe au tournant
Préface
Les configurations statiques & dynamiques
Les configurations statiques
Les configurations dynamiques
KDM
Codes
Analyse et données
Analyse des données D-BOX
Notes
MXF : Misc
MXF : Codes & Fichiers 6
JS-MXF
Récupération de l'identifiant d'un MXF (asdcplib)
Récupération de l'identifiant d'un MXF (Python)
Récupération de la Cryptographic-KeyID d'un MXF (asdcplib)
Récupération de la Cryptographic-KeyID d'un MXF (Python)
Afficher un SMPTE Universal Label - 16 octets (Python)
Afficher un SMPTE Universal Label - 12 octets (Python)
BER : Déterminer si BER est short form ou long form (C/C++)
BER : Retourner la taille du BER selon son code d'entête (C/C++)
BER : Calculer la taille (C/C++)
BER : Calculer la taille venant d'un BER 0x83 (en Python)
is SMTPE Universal Label (C/C++)
Afficher un SMPTE Universal Label - 16 octets (C/C++)
Lire un MXF et afficher Universal Label, taille et partie des données (C/C++)
Cryptographie
XOR
Chiffrement AES-128-CBC
Déchiffrement AES-128-CBC
Processus de déchiffrement de la Value du KLV Encrypted Essence Container
Création d'un MXF chiffré (asdcplib)
Création d'un MXF chiffré avec Plaintext Offset (asdcplib)
Extraction des essences d'un MXF chiffré (asdcplib) :
Extraction des essences d'un MXF chiffré (mxf-analyzer)
Création d'un MXF chiffré avec ASDCPlib (C++)
Fichiers
Cryptographie in a DCP
Cryptography : Preface
Differences between symmetric and asymmetric cryptography
The encryption workflow of a DCP
Chapters on cryptography related to the DCP
Algorithms and methods used
Future development(s)
Cryptographie : L'algorithme symétrique AES-CBC
Les différentes étapes d'un chiffrement AES-CBC
À l'intérieur du CBC
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Un exemple concret
En résumé
Chapitres connexes
Références
Cryptographie : L'algorithme asymétrique RSA 1
Préface
Les différents types de fichiers RSA
Assets
Chapitres connexes
References
Notes
La cryptographie appliquée dans un MXF 3
Aperçu de l'intérieur des MXF
Les éléments nécessaires
La cryptographie utilisée
A l'intérieur des KLV chiffrés
Etude de la Value d'un KLV chiffré
Etude d'un KLV chiffré normal
Etude de la Value d'un KLV chiffré avec Plaintext Offset
Beyond the Value
Les KLV Headers en détail
Message Integrity Code (MIC)
Ecrire nos propres KLV cryptographiques
Le padding cryptographique et la limite de la bande passante
Conclusion
Annexe : Codes et techniques
Annexe : Identifiants UL & Label
Annexe : Samples
Annexe : Des tailles fixes dans un Variable-Length Pack ?
Références
Notes
KDM : Digital Keys of films
KDM : Key Delivery Message 1
SMPTE standards
KDM principle
Inside a KDM
Subchapiters
Related Chapters
Notes
KDM : Authenticated Public 2
Préface
A l'intérieur d'AuthenticatedPublic
A l'intérieur de KDMRequiredExtensions
Recipient: les informations sur le destinataire
CompositionPlaylistId : l'identifiant de la CPL lié au KDM
ContentTitleText : le nom du KDM
ContentAuthenticator (optionnel)
ContentKeysNotValid : la gestion des droits à peu de frais
AuthorizedDeviceInfo
KeyIdList : la liste des identifiants des clefs
KeyType : le type de l'asset lié à la clef
KeyId : l'identifiant de la clef de l'asset chiffré
ForensicMarkFlag : les options du KDM
NonCriticalExtensions : les extensions propriétaires
Sous chapitres
Chapitres connexes
Notes
KDM : Authenticated Private 1
Préface
A l'intérieur d'AuthenticatedPrivate
Les EncryptedKeys et leur CipherValue
Comment déchiffrer une CipherValue
Lecture de CipherValue :
Créer une CipherValue
Sous chapitres
Chapitres connexes
Notes
KDM : Signature
Préface
A l'intérieur de Signature
A l'intérieur de SignedInfo
A l'intérieur de SignatureValue
A l'intérieur de KeyInfo
Sous chapitres
Chapitres connexes
Notes
KDM : Codes & Fichiers 1
Déchiffrer une CipherValue
Déchiffrer une CipherValue
Ouvrir tous les CipherValue d'un KDM :
Créer une CipherValue (sans la structure KDM)
Créer une CipherValue (via OpenSSL)
XMLSec: La base des signatures numériques du KDM
Générer les Signatures (DigestValue + SignatureValue) d'un KDM
Vérifier les Signatures (DigestValue + SignatureValue) d'un KDM
Vérifier les Signatures (via OpenSSL)
Créer un DigestValue (via OpenSSL)
Créer une DigestValue (via OpenSSL)
Créer une SignatureValue (via OpenSSL)
Canonicalize XML C14N (Python)
Sous chapitres
Chapitres connexes
DKDM
Certificates : Digital Identification Papers
Image
Imagery in Digital Cinema
Preface
The workflow : important steps in the conversion process
Linearization : from a curved shape to a straight shape
XYZ spacecolor : a colorimetric parallel universe
White point normalization : The White Fang Revange
Gamma 2.6 : from a straight shape to a curved shape
12-bit Bitdepth : tidy up the data
JPEG2000 image format : compress the data
Conclusion
References
Notes
Linearization : from a curved shape to a straight shape
Preface
What is linear and non-linear ?
The Linearization Principle
Quick example of linearization
Notes
XYZ : a colorimetric parallel universe 2
Preface
History and SMPTE choices
Inside XYZ
DCI-P3 Colorspace
Understanding matrix conversion
Conversion to XYZ
And with Imagemagick ?
Conversion from XYZ
Conversion drift
Reference matrices
The Matrix Museum
Bonus Tracks
Files and Assets
References
Notes
White point normalization
Preface
The normalization patch for the XYZ components
Explanations of this normalization
Bonus Stage : Why is the value 3960 for Y' ?
References
Notes
Gamma
Preface
Modify gamma
Pow ! Pow ! Pow ! That's the power of the funk !
Remove gamma (or to make it neutral)
How can we determine the value of the input gamma ?
DCI Gammas
Apply a gamma of 2.6
Apply a gamma of 1/2.6
Files and Assets
References
Notes
Bitdepth 12 bits
Preface
Lexique
The choice of 12-bit
Bitdepth conversion
a DCDM 16-bit image file
A classic 16-bit (or more) image file
Colors in a conversion
Technical bitdepth conversion
The magic of the [0..1] range
Conversion to a positive integer number
Archive / IMF
Files and Assets
References
Notes
JPEG2000 : Le format d'image utilisé dans le cinéma numérique 8
Préface
Les transformations par ondelettes (wavelet transform)
Les bases des ondelettes
Les ondelettes par le calcul
Les décompositions 2D - pour les images
Les fonctions et filtrages
Les sub-bands LL, HL, LH & HH
Les coefficients de filtrages (filter banks)
Petits calculs et grands coefficients
Les coefficients pour le JPEG2000 (Daubechies 9/7, LeGall 5/3)
Et la méthode Lifting ?
Fast Wavelet Transform
High Throughput JPEG 2000 (HTJ2K)
Le JPEG2000 normé pour le cinéma numérique
A l'intérieur du JPEG200 D-Cinema
Les différents KLV de métadonnées
SOC : Start of codestream (FF4F)
SIZ : Image and tile size (FF51)
COD : Coding style default (FF52)
QCD : Quantization default (FF5C)
CME : Comment and extension (FF64)
POC : Progression Order Change (FF5F)
TLM : Tile-part lengths, main header (FF55)
SOT : Start of tile-part (FF90)
SOD : Start of data (FF93)
EOC : End of codestream (FFD9)
Spécifications et obligations du JPEG2000 DCI
Codes et techniques
Lire et parser un JPEG2000 soi-même
Les outils externes pour manipuler du JPEG2000
Références
Notes
MXF : Picture 1
Preface
KLV Headers
KLV Body : Picture Essence
Code : Read and Extract the KLV "Picture Essence"
Code : Write own KLV Picture Essence
Cryptography
XYZ Colorimetry
JPEG2000 Encoding
Stereoscopic (3D)
High Frame Rate (HFR)
Notes
MXF : Picture : Stereoscopique (3D) 1
Préface
Les métadonnées
Lire et extraire les images stéréoscopiques
Les modifications dans la Composition Playlist (CPL)
Faire de la stéréoscopie sans utiliser ce workflow
Comment faire de la 3D en HFR
Samples
MXF : Picture : High Frame Rate (HFR)
Préface
High Frame Rate (HFR) & Stéréoscopie (3D)
Samples
Notes
3D 1 HFR 1
Sound
Sound in digital cinema
Main Sound : Sound Essence
Immersive Sound : Object-Based Audio Essence (OBAE)
Chapters related to sound
Notes
MXF : Sound 1
Préface
Les KLV de métadonnées (Partition Header)
Métadonnées supplémentaires : La configuration sonore & Multichannel Audio (MCA)
A l'intérieur du KLV Sound Essence
Création d'un header WAVE (Python)
Extraire la piste son au format WAV (Python)
Ecrire nos propres KLV
Techniques
Notes
MXF : Sound : Configuration Audio & Multichannel Audio (MCA)
Préface
Channel Assignment : Le point d'entrée
Les Sub-Descriptors Audios : Préface
Les Sub-Descriptors Audios : En détail
Channel Layout / Soundfield Groups Configuration : le statique dynamique statique
Conclusion
Notes
Immersive Audio Bitstream (IAB) : Le parent du son spatialisé
Préface
Normes et spécifications techniques
Spécifications techniques de l'IAB
MXF
Analyse du MXF
CPL
KDM
Références
Notes
Dolby Atmos : Le son spatialisé 1
Préface
CPL
MXF
Références
Notes
MXF : Dolby Atmos : Le son spatialisé 9
Préface
Les métadonnées
Les données
A l'intérieur du IABitstream : Le container maître de base
A l'intérieur d'une IABitstream frame : l'unité de base
Les IAElements : Les blocs de métadonnées et de données utiles
Les différents éléments : Leurs structures internes
IABitstream frame
IAElement
IA Frame
Bed Definition : le câblage des pistes (Bed) avec les assets audios
Object Definition : les métadonnées de spatialisation
Bed Remap : Configuration pour du sous-mixage
Object Zone Definition : Les zones alternatives
Authoring Tool Info : Les informations créateurs
User Data : Les métadonnées personnelles
Audio Data PCM & DLC : les containers audio
Audio Data DLC : l'élu pour le DCP-IAB !
Audio Data PCM : le recalé du DCP-IAB
L'encodage Plex : les tailles dynamiques
Analyse du MXF
Annexes
Notes
DTS-X : Le son spatialisé
Barco Auro : Le son spatialisé
Subtitle
Additional Assets
Misc

 Preface
Preface Digital Cinema Initiative (DCI) : History & Creation
Digital Cinema Initiative (DCI) : History & Creation Digital Cinema Package
Digital Cinema Package Standard and Specifications
Standard and Specifications MXF : Material Exchange Format
MXF : Material Exchange Format KLV : Key-Length-Value
KLV : Key-Length-Value KLV : Key: The Type Identifier (or Universal Label)
KLV : Key: The Type Identifier (or Universal Label) MXF : Picture
MXF : Picture Cryptography : Preface
Cryptography : Preface KDM : Key Delivery Message
KDM : Key Delivery Message DKDM
DKDM Certificates : The Basics
Certificates : The Basics Imagery in Digital Cinema
Imagery in Digital Cinema Linearization : from a curved shape to a straight shape
Linearization : from a curved shape to a straight shape XYZ : a colorimetric parallel universe
XYZ : a colorimetric parallel universe White point normalization
White point normalization Gamma
Gamma Bitdepth 12 bits
Bitdepth 12 bits MXF : Picture
MXF : Picture Sound in digital cinema
Sound in digital cinema